Atan2
定义于头文件 <cmath> 中。
描述
使用参数的符号来确定正确象限,计算 y / x 的反正切值。
该库为所有 cv-unqualified 浮点类型提供了 std::atan2 的重载,作为参数 y 和 x 的类型。 (自 C++23 起).
其他重载适用于所有其他算术类型组合。 (自 C++11 起).
声明
- C++23
- C++11
// 1)
/* floating-point-type */ atan2( /* floating-point-type */ y,
/* floating-point-type */ x );
// 2)
float atan2f( float y, float x );
// 3)
long double atan2l( long double y, long double x );
// 4)
template< class Arithmetic1, class Arithmetic2 >
/* common-floating-point-type */ atan2( Arithmetic1 y, Arithmetic2 x );
// 1)
float atan2 ( float y, float x );
// 2)
double atan2 ( double y, double x );
// 3)
long double atan2 ( long double y, long double x );
// 4)
float atan2f( float y, float x );
// 5)
long double atan2l( long double y, long double x );
// 6)
template< class Arithmetic1, class Arithmetic2 >
/* common-floating-point-type */ atan2( Arithmetic1 y, Arithmetic2 x );
参数
y, x - 浮点或整数值
返回值
如果没有错误发生,则返回 y / x (arctan(y/x)) 的反正切值,范围为 [-π, +π] 弧度。
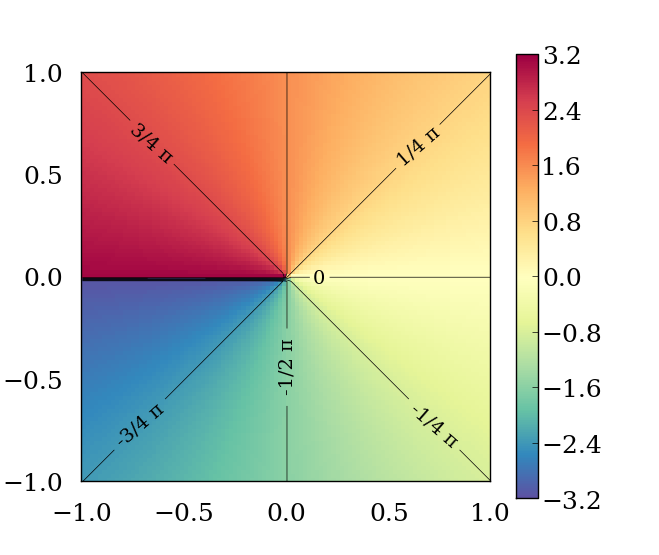
如果发生域错误,则返回实现定义的值(如果支持,返回 NaN)。
如果因下溢导致范围错误,则返回正确结果(舍入后)。
错误处理
错误按 math_errhandling 中指定的方式报告。
如果 x 和 y 都为零,可能会出现域错误。
如果实现支持 IEEE 浮点运算(IEC 60559),
- 如果
x和y都为零,则不会出现域错误。 - 如果
x和y都为零,也不会出现范围错误。 - 如果
y为零,则不会出现极点错误。 - 如果
y为±0且x为负或-0,则返回±π。 - 如果
y为±0且x为正或+0,则返回±0。 - 如果
y为±∞且x为有限值,则返回±π/2。 - 如果
y为±∞且x为-∞,则返回±3π/4。 - 如果
y为±∞且x为+∞,则返回±π/4。 - 如果
x为±0且y为负,则返回-π/2。 - 如果
x为±0且y为正,则返回+π/2。 - 如果
x为-∞且y为有限正值,则返回+π。 - 如果
x为-∞且y为有限负值,则返回-π。 - 如果
x为+∞且y为有限正值,则返回+0。 - 如果
x为+∞且y为有限负值,则返回-0。 - 如果
x或y为 NaN,则返回 NaN。
备注
std::atan2(y, x) 等同于
std::arg(std::complex<std::common_type_t<decltype(x), decltype(y)>>(x, y))
POSIX 指定,在下溢情况下,返回 y / x 的值;如果不支持,则返回一个不大于 DBL_MIN、FLT_MIN 和 LDBL_MIN 的实现定义值。
不需要严格按照 附加重载 提供附加重载。它们只需要足以确保对于它们的第一个参数 num1 和第二个参数 num2
如果 num1 或 num2 的类型是 long double,则
std::atan2(num1, num2) 与以下效果相同:
std::atan2(static_cast<long double>(num1), static_cast<long double>(num2))。
否则,如果 num1 和/或 num2 的类型是 double 或整数类型,则
std::atan2(num1, num2) 与以下效果相同:
std::atan2(static_cast<double>(num1), static_cast<double>(num2))。
num1 或 num2 的类型是 float,则:std::atan2(num1, num2) 与以下效果相同:
std::atan2(static_cast<float>(num1), static_cast<float>(num2))。 (直到 C++23)
如果 num1 和 num2 具有算术类型,则
std::atan2(num1, num2) 与以下效果相同:
std::atan2(static_cast</* 通用浮点类型 */>(num1), static_cast</* 通用浮点类型 */>(num2)).
其中 /* 通用浮点类型 */ 是 num1 和 num2 类型之间具有最大浮点转换等级和最大浮点转换子等级的浮点类型,整数类型的参数被认为具有与 double 相同的浮点转换等级。
如果不存在具有最高等级和子等级的浮点类型,则重载决议不会从提供的重载中产生可用的候选。
示例
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
void print_coordinates(int x, int y)
{
std::cout
<< std::showpos
<< "(x:" << x << ", y:"
<< y << ") cartesian is "
<< "(r:" << std::hypot(x, y)
<< ", phi:" << std::atan2(y, x)
<< ") polar\n";
}
int main()
{
// normal usage: the signs of the two arguments determine the quadrant
print_coordinates(+1, +1);
// atan2( 1, 1) = +pi/4, Quad I
print_coordinates(-1, +1);
// atan2( 1, -1) = +3pi/4, Quad II
print_coordinates(-1, -1);
// atan2(-1, -1) = -3pi/4, Quad III
print_coordinates(+1, -1);
// atan2(-1, 1) = -pi/4, Quad IV
// special values
std::cout
<< std::noshowpos
<< "atan2(0, 0) = "
<< atan2(0, 0) << '\n'
<< "atan2(0,-0) = "
<< atan2(0, -0.0) << '\n'
<< "atan2(7, 0) = "
<< atan2(7, 0) << '\n'
<< "atan2(7,-0) = "
<< atan2(7, -0.0) << '\n';
}
(x:+1, y:+1) cartesian is (r:1.41421, phi:0.785398) polar
(x:-1, y:+1) cartesian is (r:1.41421, phi:2.35619) polar
(x:-1, y:-1) cartesian is (r:1.41421, phi:-2.35619) polar
(x:+1, y:-1) cartesian is (r:1.41421, phi:-0.785398) polar
atan2(0, 0) = 0
atan2(0,-0) = 3.14159
atan2(7, 0) = 1.5708
atan2(7,-0) = 1.5708